Technology plays a huge role in our daily lives, from the simplest of apps to the most groundbreaking inventions.
Every website or piece of software that we encounter has been built by a developer—but what exactly is web development, and what do they do?
All of this will be answered in this guide to how to become a web developer.
To the outside eye, it can seem like a complicated, confusing, and somewhat inaccessible field. So, to shed some light on this fascinating industry, we’ve put together the ultimate introduction to web development and what it takes to become a fully-fledged web developer.
In this guide, we’ll go through the basics of web development in detail, and then show you the essential skills and tools you’ll need to break into the industry. If you decide web development is for you, the next step is to start learning those essential skills.
First, though, we’ll take a look at the web development industry as it stands in 2022, and consider whether web development is a smart career move—with a particular focus on the impact of the Covid-19 pandemic.
Here’s what we’ll cover:
- Is now a good time to become a web developer? (2022 update)
- Are web developers in demand right now?
- How has Covid-19 affected the industry?
- So…should you become a web developer in 2022?
- What is web development?
- Web development vs software engineering
- Types of web development
- The difference between web development and web design
- A brief history of the World Wide Web
- What does a web developer do?
- What does a frontend developer do?
- What does a backend developer do?
- What does a full-stack developer do?
- Mobile developers
- Programming languages, libraries, and frameworks
- What are languages?
- What are libraries and frameworks?
- Other web development tools
- How to become a web developer
- A rewarding job market
- Decide your learning pathway
Feel free to skip ahead using the clickable menu. Let’s go!
1. Is now a good time to become a web developer? (2022 update)
Before you jump into a new career, it’s important to consider the path ahead. Can your new industry offer you ample opportunities and stability? How likely are you to get hired after you’ve graduated from your chosen program or bootcamp?
In the wake of the past few years these questions are more important than ever. The Covid-19 pandemic has had a major impact on the economy and on the job market.
Initially in 2020 the pandemic caused hiring to slow down, as global lockdowns took effect. However the vaccine rollout and economic bounce-back led to an increase in 2021, with hiring only slowing towards the end of year. However, the report also points out that 69% of the employment shortfall comes from the leisure and hospitality, education and healthcare industries, which are particularly Covid-sensitive.
This is yet another indication that workers are gravitating towards industries and roles which are more “Covid-proof”, such as tech. With that in mind, let’s take a look at the state of the web development industry in 2022.
Are web developers in demand right now?
You’ll have noticed that, no matter what’s going on in the world around us, technology is omnipresent in our lives.
Whether it’s scrolling through our favorite social media apps, checking the news, paying for something online, or connecting with colleagues using collaboration software and tools—most of what we do relies on some form of technology. Behind this technology is a team of web developers who have not only built it, but constantly maintain it to ensure it works flawlessly.
Those who can build and maintain websites, apps, and software have a crucial role to play in today’s technology-driven world—and this is reflected in the web development job market.
But does this still stand after the unpredictable twists and turns of the past two years? In a word, yes: web developers seem to have weathered the storm relatively well. Full-stack developer came in second on indeed’s list of the best jobs, and we can see this continuing through 2022 and beyond. Just search the web for the most in-demand tech skills in 2022 and you’ll find things like web development, software engineering, cloud computing, DevOps, and problem-solving.
Full-stack development in particular will continue to be highly attractive to employers.
If you’re keen to quantify the demand for web developers, search for “web developer” or “full-stack developer” roles in your area on sites like indeed, glassdoor, and LinkedIn.
As you can see, web developers continue to be in high demand—in spite of, and perhaps even more so because of, the ongoing coronavirus pandemic. Speaking of which, how has Covid-19 affected the web development industry? Let’s take a look.
So…should you become a web developer in 2022?
So what’s the verdict? Is now a good time to become a web developer?
Looking at the job market and projected employment growth, we think the answer is pretty clear. Now is an excellent time to become a web developer!
Now more than ever, technology is pivotal to how we work, connect with loved ones, access healthcare, shop…and the list goes on. If you’re thinking about joining this exciting industry and building the technology of the future, we say go for it.
But first, let’s get back to basics. What exactly is web development, and what does a web developer actually do? Keep reading to find out.
2. What is web development?
Web development is the process of building websites and applications for the internet, or for a private network known as an intranet.
Web development is not concerned with the design of a website; rather, it’s all about the coding and programming that powers the website’s functionality.
From the most simple, static web pages to social media platforms and apps, from e-commerce websites to content management systems (CMS)—all the tools we use via the internet on a daily basis have been built by developers.
Web development vs software engineering
A hurdle to those wondering how to become a web developer is all of the jargon and buzzwords—including for the role itself! Some people introduce themselves as software engineers, others web developers, and others software developers! Are there major differences between them?
While generally software engineers tend to work more on operating systems and web developers on internet-based technologies, the reality is a little bit different. Both roles share programming languages and technologies, and as a result which term is used can depend on the location, the industry, and the company.
To give you a rough sense of the fluctuating popularity of these terms, this graph from Google \Ngram Viewer charts the evolution in popularity of the three terms as they’ve appeared in books:
 Source: Google Ngram Viewer
Source: Google Ngram Viewer
For now though what’s important is that web development and software engineering bootcamps tend to teach you the same programming tools and technologies. Once you’ve graduated and are entering the job market, remember to look more at the technologies in each job description than the title itself to see if they match your own.
Types of web development
Web development can be broken down into three layers: client-side coding (frontend), server-side coding (backend) and database technology.
Let’s take a look at each of these layers in more detail.
Client-side (Frontend)
Client-side scripting, or frontend development, refers to everything that the end user experiences directly. Client-side code executes in a web browser and directly relates to what people see when they visit a website. Things like layout, fonts, colours, menus and contact forms are all driven by the frontend.
Server-side (Backend)
Server-side scripting, or backend development, is all about what goes on behind the scenes.
The backend is essentially the part of a website that the user doesn’t actually see. It is responsible for storing and organizing data, and ensuring that everything on the client-side runs smoothly. It does this by communicating with the frontend.
Whenever something happens on the client-side—say, a user fills out a form—the browser sends a request to the server-side. The server-side “responds” with relevant information in the form of frontend code that the browser can then interpret and display.
Database technology
Websites also rely on database technology. The database contains all the files and content that are necessary for a website to function, storing it in such a way that makes it easy to retrieve, organize, edit, and save. The database runs on a server, and most websites typically use some form of relational database management system (RDBMS).
To summarize: the frontend, backend, and database technology all work together to build and run a fully functional website or application, and these three layers form the foundation of web development.
The difference between web development and web design
Just like with software engineering, you might also hear the terms “web development” and “web design” used interchangeably, but these are two very different things.
Imagine a web designer and web developer working together to build a car: the developer would take care of all the functional components, like the engine, the wheels and the gears, while the designer would be responsible for both the visual aspects—how the car looks, the layout of the dashboard, the design of the seats—and for the user experience provided by the car, so whether or not it’s a smooth drive.
Web designers design how the website looks and feels. They model the layout of the website, making sure it’s logical, user-friendly and pleasant to use.
They consider all the different visual elements, asking questions like:
- What color schemes and fonts will be used?
- What buttons, drop-down menus and scrollbars should be included, and where?
- Which interactive touchpoints does the user interact with to get from point A to B?
Web design also considers the information architecture of the website, establishing what content will be included and where it should be placed.
Web design is an extremely broad field, and will often be broken down into more specific roles such as User Experience Design, User Interface Design, and Information Architecture.
It is the web developer’s job to take this design and develop it into a live, fully functional website. A frontend developer takes the visual design as provided by the web designer and builds it using coding languages such as HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. A backend developer builds the more advanced functionality of the site, such as the checkout function on an e-commerce site.
In short, a web designer is the architect, while the web developer is the builder or engineer.
3. A brief history of the World Wide Web
The web as we know it today has been decades in the making. To help understand how web development works, let’s go back to where it all started and consider how the internet has evolved over the years.

1965: The first WAN (Wide Area Network)
The internet is essentially a network of networks, connecting all different WANs. WAN stands for Wide Area Network, a telecommunications network that spans a large geographical distance. The first WAN was established in 1965 at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. Later on, this WAN would be known as ARPANET. It was initially funded by the Advanced Research Projects Agency of the US Department of Defense.
1969: The first ever internet message
In October 1969, UCLA student Charley Kline sent the first ever internet message. He tried to send the word “login” to a computer at the Stanford Research Institute via the ARPANET network, but the system crashed after the first two letters. However, about an hour later, the system recovered and the full text was successfully delivered.
1970s: The rise of the LAN (Local Area Network)
The early 70s saw the development of several experimental LAN technologies. LAN stands for Local Area Network, a computer network that connects nearby devices in the same buildings—such as in schools, universities, and libraries. Some notable milestones include the development of Ethernet at Xerox Parc from 1973-1974, and the development of ARCNET in 1976.
1982 – 1989: Transmission Control Protocol (TCP), Internet Protocol (IP), the Domain Name System and Dial-Up Access
In 1982, Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and Internet Protocol (IP) emerged as the ARPANET protocol, and TCP/IP remains the standard internet protocol today. In 1983, the Domain Name System was established, providing a more user-friendly way of labelling and designating websites (i.e. careerfoundry.com instead of a series of numbers). In 1987, Cisco shipped its first router, and in 1989, World.std.com became the first commercial provider of dial-up internet access.
1990: Tim Berners-Lee and HTML
In 1990, Tim Berners-Lee, a scientist at CERN (the European Organization for Nuclear Research) developed HTML—HyperText Markup Language. HTML became, and still is, a fundamental building block of the internet.
1991: The World Wide Web Goes Mainstream
With the rise of the visual internet browser, the World Wide Web made its way into the mainstream. As of 2018, there are more than 4 billion internet users around the globe. This has risen to 4.66 active users in January 2021, or 59.5% of the global population, according to Statista.
4. What does a web developer do?
The role of the web developer is to build and maintain websites. Web developers can work in-house or freelance, and the specific tasks and responsibilities involved will vary depending on what kind they’ll be. If you want to learn how to become a web developer, you may have to decide whether you’d like to become a frontend, backend, or full-stack developer. Full-stack developers specialize in both the frontend and backend; we’ll go into more detail about what a full-stack developer does later on.
Web developers are responsible for building a product that meets both the client’s needs and those of the customer or end user. Web developers collaborate with stakeholders, clients and designers in order to understand the vision: how should the final website look and function?
A large part of web development also revolves around identifying and fixing bugs in order to constantly optimize and improve a website or system. Web developers are therefore keen problem solvers, regularly coming up with solutions and workarounds to keep things running smoothly.
Of course, all web developers are proficient in certain programming languages. However, different developers will work with different languages depending on their specific job title and area of expertise. Let’s take a look at the different layers of web development and the associated tasks in more detail.

What does a frontend developer do?
It is the frontend developer’s job to code the frontend of a website or application; that is, the part of the website that the user sees and interacts with. They take the backend data and turn it into something that is easily comprehensible, visually pleasing and fully functional for the everyday user. They will work from designs provided by the web designer and bring them to life using HTML, JavaScript, and CSS (more on those later!).
Frontend developer tasks
The frontend developer implements the website’s layout, interactive and navigational elements such as buttons and scrollbars, images, content and internal links (links that navigate from one page to another within the same website). Frontend developers are also responsible for ensuring optimal display across different browsers and devices. They will code the website in such a way that makes it responsive or adaptive to various screen sizes, so that the user gets the same experience whether they’re visiting the website on mobile, desktop or tablet.
Frontend developers will also carry out usability tests and fix any bugs that arise. At the same time, they will consider SEO best practices, maintain software workflow management, and develop tools that enhance how the user interacts with a website in any browser.
Curious about a career in Web Development?
What does a backend developer do?
The backend is essentially the brains behind the face (the frontend). A backend developer is therefore responsible for building and maintaining the technology needed to power the frontend, consisting of three parts: a server, an application, and a database.
The code that backend developers create ensures that everything the frontend developer builds is fully functional, and it is the backend developer’s job to make sure that the server, application, and database all communicate with each other.
So how do they do this? First, they use server-side languages such as PHP, Ruby, Python, and Java to build the application. Then they use tools like MySQL, Oracle, and SQL Server to find, save or edit data and deliver it back to the user in frontend code.
Just like frontend developers, backend developers will liaise with the client or business owner in order to understand their needs and requirements. They will then deliver these in a number of ways depending on the specifics of the project.
Backend development tasks
Typical backend development tasks include:
- creating, integrating and managing the database
- building server-side software using backend frameworks
- developing and deploying content management systems (for a blog, for example)
- working with web server technologies, API integration and operating systems
Backend developers are also responsible for testing and debugging any backend elements of a system or application.
If you want to learn more about this role, what it involves, and how to become one, check out our full backend developer guide.
What does a full-stack developer do?
A full-stack developer is someone who understands, and can work across, the “full stack” of technology: i.e. both the frontend and the backend.
Full stack developers are experts in every stage of the web development process, meaning they are well-equipped to get hands on, but can also guide on strategy and best practices.
Most full-stack developers have gathered many years of experience in a variety of different roles, giving them a solid grounding across the entire web development spectrum.
Full-stack developers are proficient in both frontend and backend languages and frameworks, as well as in server, network and hosting environments. They are also well-versed in both business logic and user experience.
Mobile developers
Web developers and software engineers may also specialize in mobile app development, either for iOS or Android.
iOS developers build apps that run with the iOS operating system—the one used by Apple devices. iOS developers tend to be fluent in Swift, the programming language that Apple created specifically for their apps.
Android developers build apps that are compatible with all Android devices, such as Samsung smartphones. Java was the official programming language for Android, but has since been replaced by Kotlin, the new kid on the block.
5. Programming languages, libraries, and frameworks
In order to build websites and apps, web developers work with languages, libraries, and frameworks.
Let’s take a look at each of these in detail, as well as some other tools that web developers use in their day-to-day work.
What are languages?
In the world of web development, languages are the building blocks that programmers use to create websites, apps and software. There are all different types of languages, including programming languages, markup languages, style sheet languages, and database languages.
Programming languages
A programming language is essentially a set of instructions and commands which tell the computer to produce a certain output.
Programmers use so-called “high-level” programming languages to write source code. High-level languages use logical words and symbols, making them easy for humans to read and understand. High-level languages can be classified as either compiled or interpreted languages.
C++ and Java, for instance, are compiled high-level languages. They are first saved in a text-based format that is comprehensible for human programmers but not for computers. In order for the computer to run the source code, it needs to be converted to a low-level language; i.e. machine code. Compiled languages tend to be used to create software applications.
Interpreted languages like Perl and PHP do not need to be compiled. Instead, source code written in these languages can be run through an interpreter—a program that reads and executes code. Interpreted languages are generally used for running scripts, such as those used to generate content for dynamic websites.
Low-level languages are those that can be directly recognized by and executed on the computer hardware; they don’t need to be interpreted or translated. Machine language and assembly language are some common examples of low-level languages.
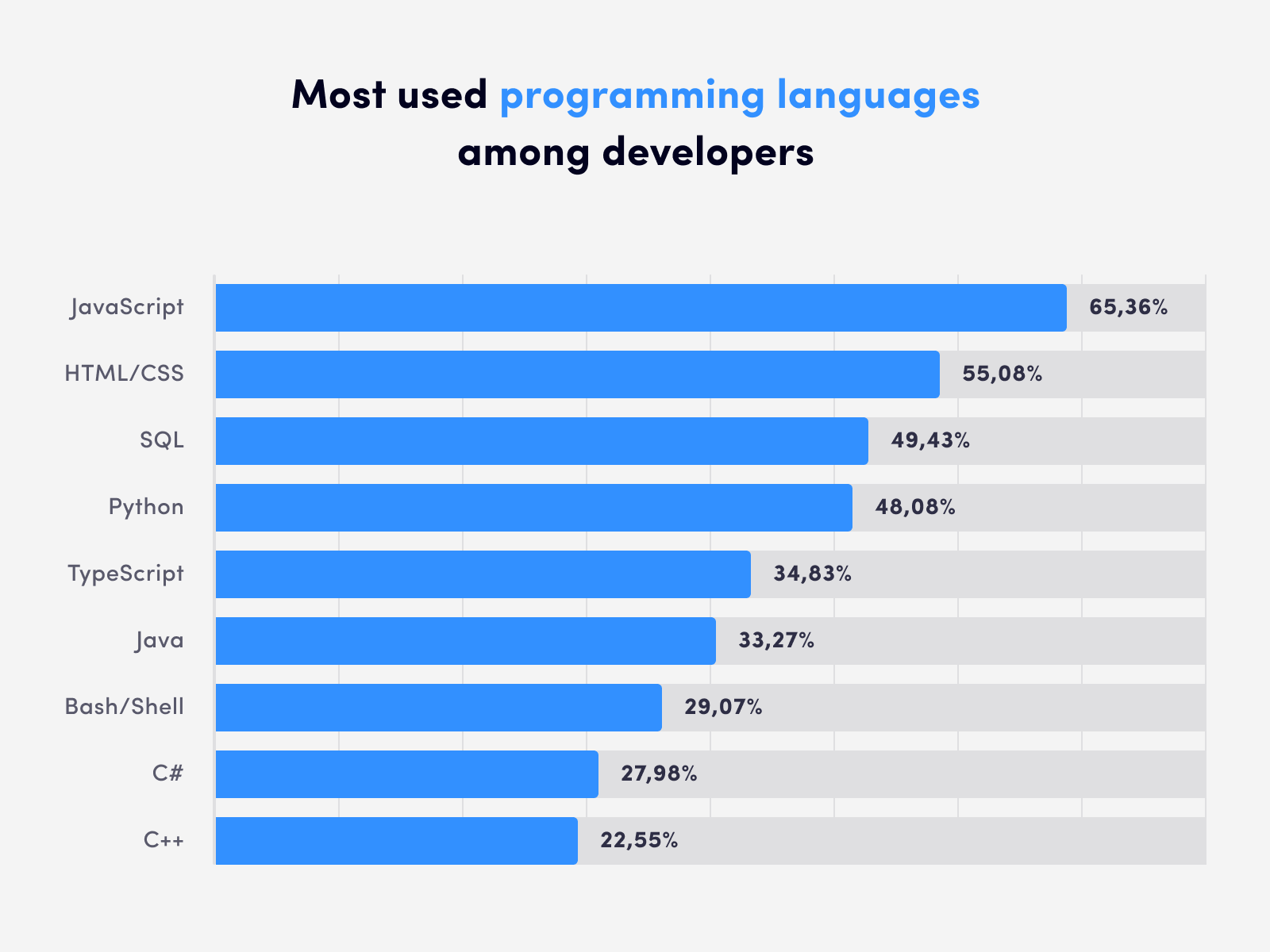
Some of the most popular programming languages of 2022 include Python, Java, C, JavaScript, C++, C#, PHP, R, and Swift.
Markup languages
Markup languages are used to specify the formatting of a text file. In other words, a markup language tells the software that displays the text how the text should be formatted. Markup languages are completely legible to the human eye—they contain standard words—but the markup tags are not visible in the final output.
The two most popular markup languages are HTML and XML. HTML stands for HyperText Markup Language and is used for the creation of websites. When added to a plain text document, HTML tags describe how this document should be displayed by a web browser. To understand how HTML works, let’s take the example of bold tags. The HTML version would be written as follows:
<b>Make this sentence bold!</b>
When the browser reads this, it knows to display that sentence in bold. This is what the user sees:
Make this sentence bold!
XML stands for eXtensible Markup Language. It is a markup language very similar to HTML. However, while HTML was designed to display data with a focus on how it looks, XML was designed purely to store and transport data. Unlike HTML, XML tags are not predefined; rather, they are created by the author of the document.
The point of XML is to simplify data sharing and transport, platform changes and data availability, as it provides a software and hardware-independent means of storing, transporting and sharing data. You can learn more about XML and how it works in W3schools’ guide.
Style sheet languages
A style sheet is basically a set of stylistic rules. Style sheet languages are used, quite literally, to style documents that are written in markup languages.
Consider a document written in HTML and styled using CSS (Cascading Style Sheets), a style sheet language. The HTML is responsible for the content and structure of the web page, while CSS determines how this content should be presented visually.
CSS can be used to add colours, change fonts, insert backgrounds and borders, as well as to style forms. CSS is also used to optimize web pages for responsive design, ensuring they adapt their layout to whatever device the user is on.
Database languages
Languages are not only used for building websites, software and apps; they are also used to create and manage databases.
Databases are used to store huge volumes of data. The Spotify music app, for example, uses databases to store music files, as well as data about the user’s listening preferences. Likewise, social media apps like Instagram use databases to store user profile information; every time a user updates their profile in some way, the app’s database will also update.
Databases are not designed to understand the same languages that apps are programmed in, so it’s essential to have a language that they do understand—like SQL, the standard language for accessing and manipulating relational databases.
As we’ explain in our beginner’s guide to SQL, the name stands for Structured Query Language. It has its own markup, and basically enables programmers to work with the data held in a database system. We’ve created a cheatsheet to get you started.
What are libraries and frameworks?
Web developers also work with libraries and frameworks. Despite much confusion, they are not the same thing—although they are both there to make the developer’s job easier.
Libraries and frameworks are essentially sets of prewritten code, but libraries are smaller and tend to be used for more specific use-cases. A library contains a collection of useful code, grouped together to be reused later. The purpose of a library is to enable developers to reach the same end goal while writing less code to get there.
Let’s take the example of JavaScript, the language, and jQuery, a JavaScript library. Rather than writing, say, ten lines of code in JavaScript, the developer can take the condensed, prewritten version from the jQuery library—saving time and effort.
A framework contains ready-made components and tools that enable the developer to write code faster, and many frameworks also contain libraries.
It gives the developer a structure to work from, and the framework you choose to work with will largely dictate the way you build your website or app, so choosing a framework is a big decision. Some popular frameworks include Bootstrap, Rails, and Angular.
The easiest way to understand libraries and frameworks is to imagine you are building a house. The framework provides the foundation and the structure, as well as instructions or guidelines for completing certain tasks.
Say you want to install an oven in your new home: you could buy the separate components and build the oven from scratch, or you could pick a ready-made oven from the store. Just like building a website, you can write the code from scratch or you can take pre-written code from a library and simply insert it.
Other web development tools
Web developers will also use a text editor, such as Atom, Sublime or Visual Studio Code, to write their code; a web browser, such as Chrome or Firefox; and an extremely crucial tool: Git!
Git is a version control system where developers can store and manage their code. As a web developer, it’s inevitable that you’ll make constant changes to your code, so a tool like Git that enables you to track these changes and reverse them if necessary is extremely valuable.
Git also makes it easier to work with other teams and to manage multiple projects at once. Git has become such a staple in the world of web development that it’s now considered really bad practice not to use it.
Another extremely popular tool is GitHub, a cloud interface for Git. While we explain more about what it is and how to use it in our GitHub guide, essentially this tool offers all the version control functionality of Git, but also comes with its own features such as bug tracking, task management and project wikis.
You can read our guide if you’re interested in learning more about the differences between Git and GitHub.
GitHub not only hosts repositories; it also provides developers with a comprehensive toolset, making it easier to follow best practices for coding. It is considered the place to be for open-source projects, and also provides a platform for web developers to showcase their skills.
6. How to become a web developer
A rewarding job market
A career in web development is challenging, financially rewarding, and has a lot to offer in terms of job security. More than that, web developer was ranked high based on salary and employment rates.
At the time of writing, the average base salary for a web developer in the Nigeria is ₦970,000 per year. Of course, salary varies depending on location, years of experience and the specific skills you bring to the table.

Once you start deciding which type of programmer you want to become, it can help to research what the average salaries for these are. Useful resources for this would be our JavaScript developer, Python developer, and full-stack developer salary guides.
Decide your learning pathway
The first step to a career in web development is to learn the necessary languages, libraries, and frameworks.
You’ll also need to familiarize yourself with some of the above-mentioned tools, as well as some common terminology. For a beginner-friendly introduction, start with these 50 web development buzzwords that all budding coders should know.
In terms of the languages you learn, it all depends on whether you want to focus on frontend, backend, or full-stack development. Regardless, all web developers should be proficient in HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, which is why most web development or software engineering programs will include them so on their curriculum.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/windows-update-restart-required-9135caaf9bc8435f996c9ff7c7731572.png)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/windows-11-settings-apps-list-b2429c83382041d685e3964d889edc21.png)


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/pixel8-6ac6481299514e17aee036b125a33366.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/pixel8andpro-a0d78f20468c406fa5dbbd72dbe0644f.jpg)







 Source: Google Ngram Viewer
Source: Google Ngram Viewer